Industrial facilities across the United States depend on reliable industrial water to keep production running. When industrial water treatment fails to align with an industrial facility’s water treatment needs, costs rise fast through downtime, equipment wear, unstable water quality and higher water consumption.
Raw water variability, weak water treatment methods and outdated industrial water treatment systems quietly strain boiler water treatment, cooling water performance and overall industrial processes.
Effective industrial water treatment protects industrial equipment, stabilizes water chemistries, supports a consistent industrial water supply and reduces long-term operational risk.
What Is Industrial Water Treatment?

Industrial water treatment refers to the treatment of water that prepares raw water for use in manufacturing and manages wastewater for safe discharge or reuse.Unlike municipal drinking water programs, industrial water treatment processes address larger volumes of water, higher contaminant loads and precise process requirements tied to industrial operations.
These water treatment methods focus on protecting industrial equipment, stabilizing process water and supporting consistent production rather than human consumption.
Many industrial water treatment systems operate under the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits with industry-specific Effluent Limitation Guidelines (ELGs). These guidelines often set more pollutant-specific limits than the g eneral local limits used by Publicly Owned Treatment Works (POTWs) for municipal and industrial wastewater.
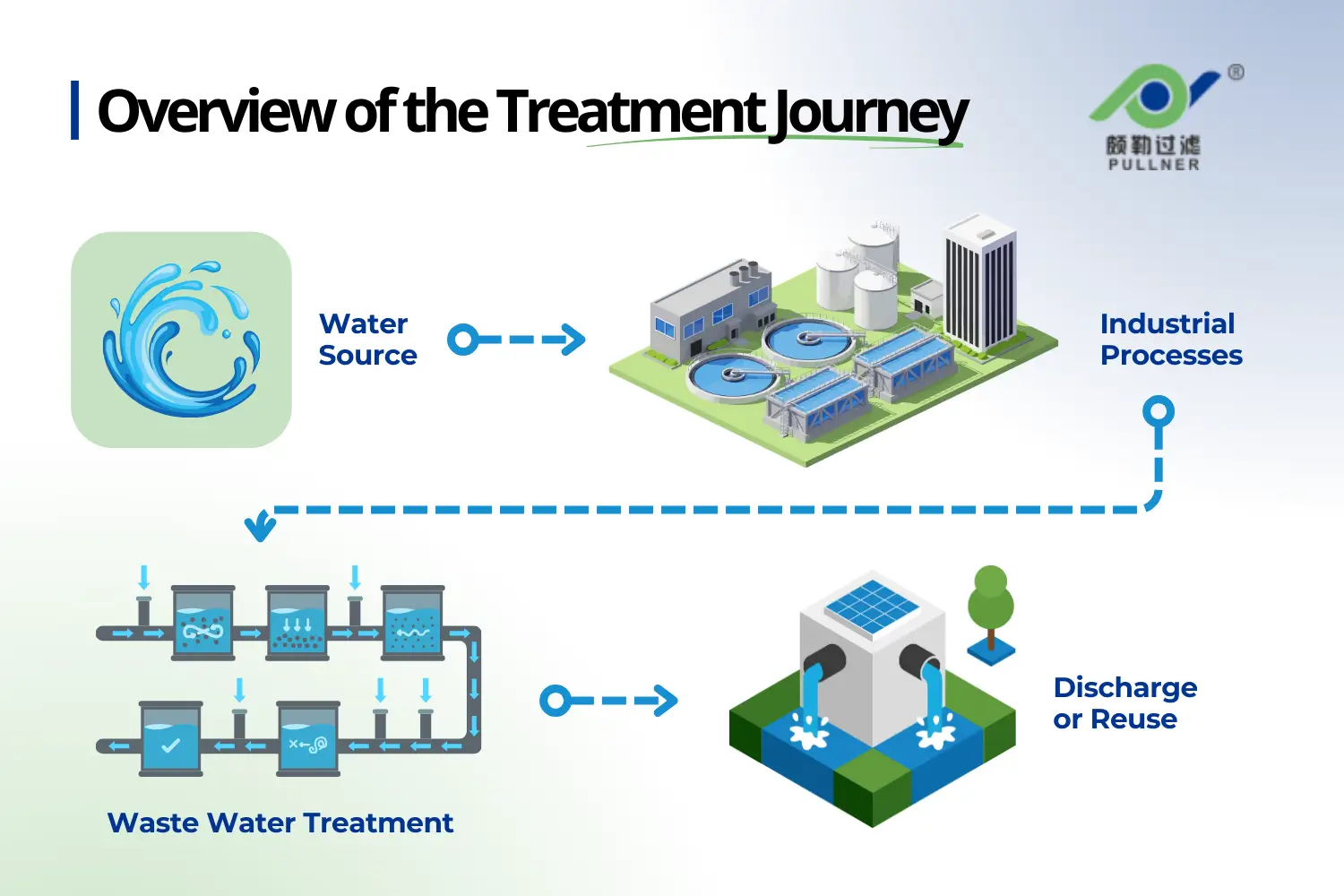
Treatment Journey Overview
Industrial facilities manage water through two coordinated treatment streams that operate within a single industrial water treatment system. Each stream supports a different stage of industrial water use and requires a structured treatment process to protect operations and meet compliance goals.
Industrial facilities typically follow a two-stream treatment journey:
- Makeup water treatment prepares raw water before use in industrial processes, supporting stable water quality and a reliable industrial water supply.
- Wastewater treatment manages wastewater after use, controlling contaminants before discharge, reuse, or transfer to wastewater treatment plants.
Integrated multi-step systems combine multiple water treatment techniques and treatment technologies into a unified water treatment system that operates across the full water and wastewater treatment cycle.
Makeup Water Treatment Steps
The makeup water treatment process involves several critical steps that prepare raw water for use in industrial processes. Each stage ensures that water meets the required quality for efficient operations and equipment protection.
Makeup water treatment includes these key steps:
- Intake and initial screening remove large debris and particles from the raw water, protecting downstream equipment.
- Primary solids removal (clarification) uses gravity or chemical treatment to settle out larger solids, ensuring water clarity.
- Filtration and fine particle removal targets smaller particles, improving water quality and preventing blockages in pipes and equipment.
- Softening and scale control reduce hardness by removing calcium and magnesium ions, which can cause scaling in boilers and pipes.
- Corrosion control and conditioning add chemicals to prevent damage to metal surfaces and extend the life of industrial equipment.
- Disinfection and biological control eliminate harmful microorganisms, ensuring safe water use in industrial operations.
- Advanced treatment (membranes, polishing) further refines water quality, often using technologies like reverse osmosis or additional filtration for high-purity water.
Wastewater Treatment Steps
The wastewater treatment process follows several key stages designed to ensure that industrial wastewater meets discharge or reuse standards.
Most wastewater systems follow this process:
- Collection and equalization gather and stabilize wastewater flows, ensuring consistent treatment.
- Primary solids removal uses settling or mechanical methods to remove large particles and settleable matter from the wastewater.
- Biological treatment (organic removal) uses microorganisms to break down organic matter, reducing pollutants.
- Secondary clarification or filtration separates fine solids and remaining contaminants from the treated wastewater.
- Final disinfection eliminates any remaining pathogens to ensure the treated water is safe for discharge or reuse.
- Compliance testing before discharge verifies that wastewater meets regulatory requirements for safe discharge or reuse.
- Optional advanced treatment for reuse applies additional processes, like reverse osmosis or polishing, to meet higher purity standards for water reuse.
Where It Shows Up in a Plant
Industrial water treatment is essential in several key areas of a plant, ensuring equipment longevity and operational efficiency.
- Boiler water must be carefully treated to prevent corrosion, scaling and sediment buildup. Softening, pH control and oxygen scavengers are common methods to maintain water quality and reduce the risk of downtime and repair costs.
- Cooling water is used to regulate temperature, requiring treatment to control biofilm, scaling and corrosion. Maintaining the quality of cooling water ensures efficient heat transfer and protects vital systems from damage.
- Process water and rinse water are used during manufacturing and cleaning. Treatment is necessary to prevent contamination and ensure the final product meets quality standards. This may involve filtration, disinfection and chemical conditioning.
- Wastewater and effluent are produced after industrial activities. These need thorough treatment to remove contaminants before discharge or reuse. Common methods include primary solids removal, biological treatment and final disinfection. Advanced techniques, like reverse osmosis, may also be employed for reuse in other processes, such as cooling.
Why It Matters for Businesses
Industrial water treatment is essential for businesses, delivering multiple benefits that directly affect operational efficiency, cost management and long-term sustainability.

Water Management
Water management systems ensure the proper treatment of industrial water, which helps extend the lifespan of equipment like boilers, cooling towers and pipes.
By preventing corrosion and scaling, businesses reduce maintenance costs and downtime. This allows equipment to operate at peak efficiency, minimizing unexpected failures that disrupt operations.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Effective industrial wastewater treatment reduces energy consumption in key systems. For example, cooling water treatment minimizes fouling, allowing heat exchangers and cooling towers to work more efficiently, which directly lowers energy costs.
By treating water properly before reuse, businesses can reduce the strain on their energy-intensive systems, driving down operational expenses.
Wastewater Treatment Systems
Wastewater treatment systems ensure compliance with industry regulations, such as NPDES permits, which dictate specific pollutant limits.
By adhering to these guidelines, businesses avoid costly fines and operational disruptions due to non-compliance. Routine wastewater testing ensures that businesses meet discharge or recycling standards before releasing water into the environment or reuse systems.
Water Treatment Technologies
Integrating advanced water treatment technologies into production lines not only supports regulatory compliance but also drives sustainability.
Technologies like reverse osmosis and membranes enhance water quality for reuse, which helps businesses reduce the volume of fresh water needed. By reusing treated wastewater, businesses decrease their overall water consumption, saving costs on procurement while supporting sustainability goals.
Water Treatment Services
Water treatment services that combine industrial water and wastewater treatment help businesses manage their water use more efficiently.
By reducing wastewater generation and increasing water reuse, companies can conserve valuable resources, reduce environmental impact and improve their standing in an increasingly eco-conscious market. These solutions also ensure long-term cost savings by minimizing water purchase and waste disposal costs.
Common Challenges
Industrial water treatment faces several challenges that complicate operations and increase costs. Overcoming these obstacles requires effective strategies and well-designed water and wastewater treatment systems.
Variable Source Water
Industrial water treatment methods must address large volumes of water with varying contaminant levels.
The quality of source water fluctuates due to environmental factors, making it difficult to apply a consistent treatment approach. Treatment systems need to adapt to these changes to ensure consistent quality and efficient operation, which can drive up costs when source water quality is unpredictable.
Complex Discharge Regulations
Wastewater discharge regulations can be complex and vary by region, industry, and pollutant type.
Compliance with local, state and federal guidelines often demands advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Facilities must ensure their treatment facilities can meet the required effluent limits, especially under NPDES permits, and this adds significant operational complexity and costs.
Aging Systems
Many industrial water treatment systems are outdated, leading to inefficiencies and high maintenance costs. Older systems may struggle with handling large volumes of water, causing frequent downtime and repairs.
Upgrading these systems with newer water treatment technologies is a necessary but costly investment for long-term operational efficiency.
Limited Expertise
A lack of in-house expertise can hinder effective industrial water treatment methods. Managing water quality and optimizing water and energy use requires skilled personnel familiar with the latest treatment technologies.
Without proper training, businesses may struggle to implement efficient systems, leading to higher costs and potential regulatory risks.
Smart Monitoring and Automation: Keeping Systems Running Smoothly
Effective water treatment in industrial settings relies on automation and continuous monitoring to ensure consistent water quality and process efficiency. By utilizing real-time data, facilities can optimize water processes and minimize operational disruptions.
- Continuous sensors monitor key parameters such as pH, conductivity and flow in both makeup water and wastewater streams. These sensors allow for instant adjustments to ensure water quality remains within the required specifications for industrial operations.
- Feed water quality is continuously assessed to ensure that treatment chemicals are applied accurately. Automated systems adjust chemical dosing in real time, optimizing the use of water treatment chemicals for effective results and reducing waste.
- Automated monitoring systems also track chemical levels, ensuring that they are within safe operating ranges and not exceeding regulatory limits. This reduces the risk of chemical imbalances that could harm equipment or violate discharge regulations.
- For surface water sources, automated sensors detect changes in water quality, triggering adjustments to the treatment process before water enters the system. This helps ensure the water remains suitable for industrial use without compromising the equipment or processes.
Industrial Water Treatment FAQs
What’s the main difference between industrial and municipal water treatment?
Industrial water treatment protects equipment and meets process needs, with industrial dischargers often holding NPDES permits that include pollutant-specific effluent limits. Municipal treatment focuses on producing safe drinking water for the public.
Why is proper water treatment critical for industrial plants?
It prevents scaling, extends equipment life, reduces energy use, ensures compliance and supports water reuse for sustainability and cost savings.
What role does automation play in industrial water treatment?
Automation allows real-time monitoring, precise chemical dosing, early issue detection and accurate compliance records, improving efficiency and reliability.
Understand industrial water treatment, its role in protecting equipment, meeting process needs and complying with strict regulations.
Back to Top: Industrial Water Treatment: How It Works and Why It Matters
